To ensure that the salary run for the month of December 2020 and/or period 2020-13 (thirteenth-month payment) is processed before Christmas, please submit any changes for this period no later than 16 December 2020. If this is a problem, contact your payroll consultant.
Because of the many legislative changes in 2021, the processing time in January 2021 will be longer than you are accustomed to from us. Please submit the January 2021 changes earlier, if possible. If this is a problem, contact your payroll consultant.
For the correct payment of contributions to the tax authorities, we need the Whk percentage specified in the Return to Work Fund decision. Please send a copy of this decision to your designated payroll consultant as soon as possible.

As you are aware, any settlement of the WKR for 2020 must be included in the wage tax and national insurance contributions return for the month of February 2021, to be paid by 31 March 2021. This settlement consists partly of items from payroll accounting and items from financial accounting. We have identified the items from payroll accounting but are unaware of any items in the 2020 financial accounting that fall under the tax-free margin of the WKR. Please let us know before 10 February 2021 if there are any items in the 2020 financial accounting that fall under the tax-free margin of the WKR with their amounts. Examples include the costs of a staff party, Christmas gifts, flowers for a sick employee (above €25.00 including VAT), gym subscriptions, and so on.
If you have applied for the care bonus for your employees, we recommend you have a WKR scan performed. Contact your payroll consultant for this purpose. If we do not receive a response from you by 28 February 2021, we will assume that there are no items in the 2020 financial accounting that fall under the tax-free margin of the WKR.
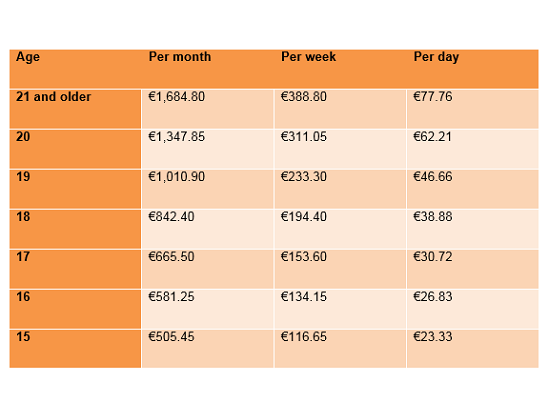
As from 1 July 2019, every employee aged 21 and older is entitled to the full statutory minimum wage. The statutory minimum wage amounts apply for a full working week. Here are the minimum wage amounts as from 1 January 2021.
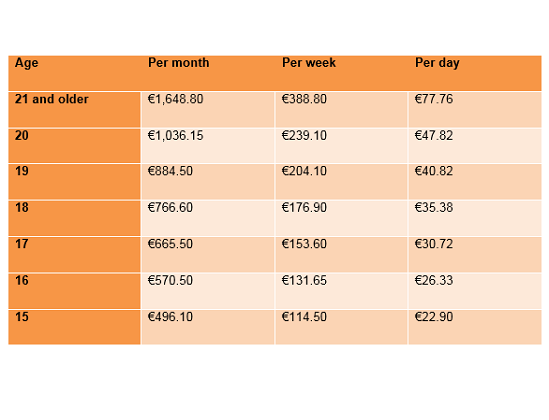
Here are the gross minimum wage amounts for apprentices working on the block-or-day release training pathway (BBL). These amounts apply as from 1 January 2021.
It was announced last year that the additional tax liability for the private use of electric cars would be gradually increased. As from 1 January 2021, the additional tax liability for the private use of electric cars is 12% (2020: 8%) on a maximum of €40,000 (2020: €45,000). If the listed value is higher than €40,000, the normal additional tax liability of 22% applies to the amount exceeding €40,000.
The additional tax liability will be increased to 16% in 2022. In 2025, it will rise to 17%. The maximum listed value to which the lower additional tax liability applies will not increase and will remain €40,000. A new provision as from 1 January 2021 is that the maximum listed value does not apply to solar cars, powered by integrated solar panels. By doing this, the government aims to anticipate the development of the car market.
Because of the coronavirus crisis, employers may consider the days that employees work from home as travel days in 2020. This measure allows employers to continue paying the fixed travel allowance tax-free. The fixed expense allowance may also continue to be paid tax-free if the employee was entitled to it unconditionally before 13 March 2020.
From 1 January 2021, working-from-home days may no longer be regarded as travel days. This means that employees’ current travel patterns need to be analysed. Based on their current travel pattern, it must be determined whether a fixed travel allowance may still be paid tax-free. This can be determined by testing whether the employee meets the 36-weeks or 128-days requirement. If an employee travels to a fixed place of work for 36 weeks or 128 days a year, a fixed travel allowance may be paid tax-free. If this is not the case, travel expenses must be reimbursed based on actual costs or expense claims.
For implementation reasons, it has been decided to bring forward the original end date of the life-course savings scheme. The new end date is 1 November 2021. If there is still a balance on your life-course savings account on 1 November 2021, your bank will pay that amount as a lump sum and transfer the balance to you after deducting tax. This may affect your income taxes. Contact your payroll consultant about the options for early withdrawal of your life-course savings account balance.
The work-related expenses scheme (WKR) is mandatory for all employers. The WKR allows you to spend part of your total taxable wage (the tax-free margin) on tax-free allowances, benefits in kind, and provisions for your employees.

You do not pay wage tax on the amount that falls within the tax-free margin. On the amount above the tax-free margin, you pay wage tax in the form of a final levy. You do not have to pay national insurance contributions, employee insurance scheme contributions, and the employer’s levy under the Healthcare Insurance Act (Zvw) on this amount or withhold Zvw contributions.
You can reimburse, provide, or make certain items available to your employees tax-free. Examples include travel expenses, telephones, or computers. You do this through targeted exemptions and nil valuations. These are not deducted from your tax-free margin.
If you have employees, you can remunerate them tax-free because of the work-related costs scheme (WKR). You may also reimburse something that may benefit your employees privately, such as a sports subscription or Christmas hamper. In 2021, you may give tax-free allowances of up to 1.7% on the first €400,000 of the wage bill (wages of all employees), plus 1.18% (2020: 1.2%) of the wage bill exceeding €400,000. This is the tax-free margin.

If you are a DGA of a private limited company whose turnover has been severely affected by the coronavirus crisis, you may lower your usual salary in that capacity. This can be done without consulting the tax inspector first.
However, you must meet these conditions:
Usual salary 2020 = A x B/C
You may also demonstrate that the usual salary must be lower than the salary according to this calculation. If in doubt or in special situations, contact your payroll consultant or tax office.
Note:
Salary already paid cannot be reduced retroactively. Accordingly, if you have received your regular salary in recent months, this cannot be reversed to use the above option.
You can deduct expense allowances from your usual salary if they can be individualised. It does not matter whether the expense allowances are taxed or tax-free. This could be a tax-free allowance for meals or travel expenses. The additional tax liability for private use of the company car also counts towards the usual salary. Example: for a €60,000 car with an additional tax liability of 22%, you can lower your usual salary by €13.200 (€60,000 x 22%).
By reducing your usual salary, which must amount to at least €46,000 in 2020, you pay less tax in box 1 as a DGA.